 |
Jolt Physics
A multi core friendly Game Physics Engine
|
 |
Jolt Physics
A multi core friendly Game Physics Engine
|
#include <BodyLockMulti.h>
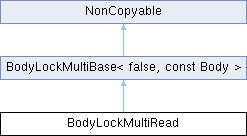
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from BodyLockMultiBase< false, const Body > Public Types inherited from BodyLockMultiBase< false, const Body > | |
| using | MutexMask |
| Redefine MutexMask. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from BodyLockMultiBase< false, const Body > Public Member Functions inherited from BodyLockMultiBase< false, const Body > | |
| BodyLockMultiBase (const BodyLockInterface &inBodyLockInterface, const BodyID *inBodyIDs, int inNumber) | |
| Constructor will lock the bodies. | |
| void | ReleaseLocks () |
| Explicitly release the locks on all bodies (normally this is done in the destructor) | |
| ~BodyLockMultiBase () | |
| Destructor will unlock the bodies. | |
| int | GetNumBodies () const |
| Returns the number of bodies that were locked. | |
| const Body * | GetBody (int inBodyIndex) const |
| Access the body (returns null if body was not properly locked) | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from NonCopyable Public Member Functions inherited from NonCopyable | |
| NonCopyable ()=default | |
| NonCopyable (const NonCopyable &)=delete | |
| void | operator= (const NonCopyable &)=delete |
A multi body lock takes a number of body IDs and locks the underlying bodies so that other threads cannot access its members
The common usage pattern is:
BodyLockInterface lock_interface = physics_system.GetBodyLockInterface(); // Or non-locking interface if the lock is already taken
const BodyID *body_id = ...; // Obtain IDs to bodies
int num_body_ids = ...;
// Scoped lock
{
BodyLockMultiRead lock(lock_interface, body_ids, num_body_ids);
for (int i = 0; i < num_body_ids; ++i)
{
const Body *body = lock.GetBody(i);
if (body != nullptr)
{
const Body &body = lock.Body();
// Do something with body
...
}
}
}