 |
Jolt Physics
A multi core friendly Game Physics Engine
|
 |
Jolt Physics
A multi core friendly Game Physics Engine
|
#include <PathConstraint.h>
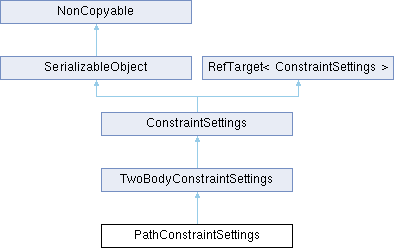
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | SaveBinaryState (StreamOut &inStream) const override |
| Saves the contents of the constraint settings in binary form to inStream. | |
| virtual TwoBodyConstraint * | Create (Body &inBody1, Body &inBody2) const override |
| Create an instance of this constraint. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from TwoBodyConstraintSettings Public Member Functions inherited from TwoBodyConstraintSettings | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings Public Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from SerializableObject Public Member Functions inherited from SerializableObject | |
| virtual | ~SerializableObject ()=default |
| Destructor. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > Public Member Functions inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > | |
| RefTarget ()=default | |
| Constructor. | |
| RefTarget (const RefTarget &) | |
| ~RefTarget () | |
| assert no one is referencing us | |
| void | SetEmbedded () const |
| RefTarget & | operator= (const RefTarget &) |
| Assignment operator. | |
| uint32 | GetRefCount () const |
| Get current refcount of this object. | |
| void | AddRef () const |
| Add or release a reference to this object. | |
| void | Release () const |
Public Attributes | |
| RefConst< PathConstraintPath > | mPath |
| The path that constrains the two bodies. | |
| Vec3 | mPathPosition = Vec3::sZero() |
| The position of the path start relative to world transform of body 1. | |
| Quat | mPathRotation = Quat::sIdentity() |
| The rotation of the path start relative to world transform of body 1. | |
| float | mPathFraction = 0.0f |
| The fraction along the path that corresponds to the initial position of body 2. Usually this is 0, the beginning of the path. But if you want to start an object halfway the path you can calculate this with mPath->GetClosestPoint(point on path to attach body to). | |
| float | mMaxFrictionForce = 0.0f |
| Maximum amount of friction force to apply (N) when not driven by a motor. | |
| MotorSettings | mPositionMotorSettings |
| In case the constraint is powered, this determines the motor settings along the path. | |
| EPathRotationConstraintType | mRotationConstraintType = EPathRotationConstraintType::Free |
| How to constrain the rotation of the body to the path. | |
 Public Attributes inherited from ConstraintSettings Public Attributes inherited from ConstraintSettings | |
| bool | mEnabled = true |
| If this constraint is enabled initially. Use Constraint::SetEnabled to toggle after creation. | |
| uint32 | mConstraintPriority = 0 |
| uint | mNumVelocityStepsOverride = 0 |
| Used only when the constraint is active. Override for the number of solver velocity iterations to run, 0 means use the default in PhysicsSettings::mNumVelocitySteps. The number of iterations to use is the max of all contacts and constraints in the island. | |
| uint | mNumPositionStepsOverride = 0 |
| Used only when the constraint is active. Override for the number of solver position iterations to run, 0 means use the default in PhysicsSettings::mNumPositionSteps. The number of iterations to use is the max of all contacts and constraints in the island. | |
| float | mDrawConstraintSize = 1.0f |
| Size of constraint when drawing it through the debug renderer. | |
| uint64 | mUserData = 0 |
| User data value (can be used by application) | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | RestoreBinaryState (StreamIn &inStream) override |
| This function should not be called directly, it is used by sRestoreFromBinaryState. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings Protected Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings | |
| ConstraintSettings ()=default | |
| Don't allow (copy) constructing this base class, but allow derived classes to (copy) construct themselves. | |
| ConstraintSettings (const ConstraintSettings &)=default | |
| ConstraintSettings & | operator= (const ConstraintSettings &)=default |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from SerializableObject Protected Member Functions inherited from SerializableObject | |
| SerializableObject ()=default | |
| Don't allow (copy) constructing this base class, but allow derived classes to (copy) construct themselves. | |
| SerializableObject (const SerializableObject &)=default | |
| SerializableObject & | operator= (const SerializableObject &)=default |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from ConstraintSettings Public Types inherited from ConstraintSettings | |
| using | ConstraintResult = Result<Ref<ConstraintSettings>> |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings Static Public Member Functions inherited from ConstraintSettings | |
| static ConstraintResult | sRestoreFromBinaryState (StreamIn &inStream) |
| Creates a constraint of the correct type and restores its contents from the binary stream inStream. | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > Static Public Member Functions inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > | |
| static int | sInternalGetRefCountOffset () |
| INTERNAL HELPER FUNCTION USED BY SERIALIZATION. | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > Protected Attributes inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > | |
| atomic< uint32 > | mRefCount |
| Current reference count. | |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > Static Protected Attributes inherited from RefTarget< ConstraintSettings > | |
| static constexpr uint32 | cEmbedded |
| A large value that gets added to the refcount to mark the object as embedded. | |
Path constraint settings, used to constrain the degrees of freedom between two bodies to a path
The requirements of the path are that:
The reason for all this is that the constraint acts like a slider constraint with the sliding axis being the tangent vector (the assumption here is that delta time will be small enough so that the path is linear for that delta time).
|
overridevirtual |
Create an instance of this constraint.
Implements TwoBodyConstraintSettings.
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
This function should not be called directly, it is used by sRestoreFromBinaryState.
Reimplemented from ConstraintSettings.
|
overridevirtual |
Saves the contents of the constraint settings in binary form to inStream.
Reimplemented from ConstraintSettings.
| float PathConstraintSettings::mMaxFrictionForce = 0.0f |
Maximum amount of friction force to apply (N) when not driven by a motor.
| RefConst<PathConstraintPath> PathConstraintSettings::mPath |
The path that constrains the two bodies.
| float PathConstraintSettings::mPathFraction = 0.0f |
The fraction along the path that corresponds to the initial position of body 2. Usually this is 0, the beginning of the path. But if you want to start an object halfway the path you can calculate this with mPath->GetClosestPoint(point on path to attach body to).
| Vec3 PathConstraintSettings::mPathPosition = Vec3::sZero() |
The position of the path start relative to world transform of body 1.
| Quat PathConstraintSettings::mPathRotation = Quat::sIdentity() |
The rotation of the path start relative to world transform of body 1.
| MotorSettings PathConstraintSettings::mPositionMotorSettings |
In case the constraint is powered, this determines the motor settings along the path.
| EPathRotationConstraintType PathConstraintSettings::mRotationConstraintType = EPathRotationConstraintType::Free |
How to constrain the rotation of the body to the path.